Ⅰ.What is non-destructive testing?
Generally speaking, non-destructive testing uses the characteristics of sound, light, electricity and magnetism to detect the location, size, quantity, nature and other related information of near-surface or internal defects on the surface of the material without damaging the material itself.Non-destructive testing aims to detect the technical status of materials, including whether they are qualified or have remaining service life, without affecting the future performance of the materials.The common non-destructive testing methods include ultrasonic test, electromagnetic test, and magnetic particle test, among which Ultrasonic Test is one of the most commonly used methods.
Ⅱ.Five common non-destructive testing methods:
Ultrasonic Test is a method that uses the characteristics of ultrasonic waves to propagate and reflect in materials to detect internal defects or foreign objects in materials. It can detect various defects, such as cracks, pores, inclusions, looseness, etc. Ultrasonic flaw detection is suitable for various materials, and can also detect the thickness of materials, such as metals, non-metals, composite materials, etc. It is one of the most commonly used methods in non-destructive testing.
Why are thick steel plates, thick-walled pipes and large-diameter round bars more suitable for UT test?
① When the thickness of the material is large, the possibility of internal defects such as pores and cracks will increase accordingly.
②Forgings are manufactured through a forging process, which may cause defects such as pores, inclusions, and cracks within the material.
③Thick-walled pipes and large-diameter round rods are usually used in demanding engineering structures or situations that bear high stress. UT test can penetrate deep into the material and find possible internal defects, such as cracks, inclusions, etc., which is crucial to ensuring the integrity and safety of the structure.
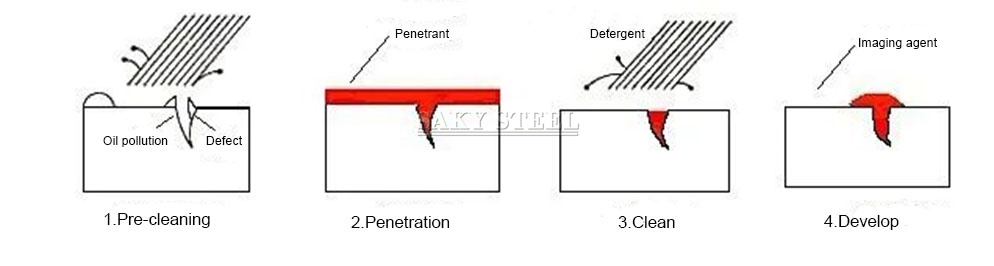
2.PENETRANT TEST definition
Applicable scenarios for UT Test and PT Test
UT test is suitable for detecting internal defects of materials, such as pores, inclusions, cracks, etc. UT test can penetrate the material thickness and detect defects inside the material by emitting ultrasonic waves and receiving reflected signals.
PT test is suitable for detecting surface defects on the surface of materials, such as pores, inclusions, cracks, etc. PT testing relies on liquid penetration into surface cracks or defects and uses a color developer to display the location and shape of defects.
UT test and PT test have their own advantages and disadvantages in practical applications. Choose the appropriate testing method according to different testing needs and material characteristics to obtain better testing results.
3.Eddy Current Test
(1)Introduction to ET Test
ET Test uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to bring an alternating current-carrying test coil close to a conductor workpiece to generate eddy currents. Based on the changes in eddy currents, the properties and status of the workpiece can be inferred.
(2)Advantages of ET Test
ET Test does not require contact with the workpiece or medium, the detection speed is very fast, and it can test non-metallic materials that can induce eddy currents, such as graphite.
(3)Limitations of ET Test
It can only detect surface defects of conductive materials. When using a through-type coil for ET, it is impossible to determine the specific location of the defect on the circumference.
(4)Costs and benefits
ET Test has simple equipment and relatively easy operation. It does not require complicated training and can quickly perform real-time testing on site.
The basic principle of PT test: after the surface of the part is coated with fluorescent dye or colored dye, the penetrant can penetrate into the surface opening defects under a period of capillary action; after removing the excess penetrant on the surface of the part, the part can be Apply developer to the surface. Similarly, under the action of the capillary, the developer will attract the penetrant retained in the defect, and the penetrant will seep back into the developer. Under a certain light source (ultraviolet light or white light), the traces of the penetrant at the defect will be displayed. , (yellow-green fluorescence or bright red), thereby detecting the morphology and distribution of defects.
4.Magnetic Particle Testing
Magnetic Particle Testing" is a commonly used non-destructive testing method for detecting surface and near-surface defects in conductive materials, particularly for detecting cracks. It is based on the unique response of magnetic particles to magnetic fields, allowing for the effective detection of subsurface flaws.
5.RADIOGRAPHIC TEST
(1)Introduction to RT Test
X-rays are electromagnetic waves with extremely high frequency, extremely short wavelength, and high energy. They can penetrate objects that cannot be penetrated by visible light, and undergo complex reactions with materials during the penetration process.
(2)Advantages of RT Test
RT Test can be used to detect internal defects of materials, such as pores, inclusion cracks, etc., and can also be used to evaluate the structural integrity and internal quality of materials.
(3)The principle of RT Test
RT Test detects defects inside the material by emitting X-rays and receiving reflected signals. For thicker materials, UT test is an effective means.
(4)Limitations of RT Test
RT Test has certain limitations. Due to its wavelength and energy characteristics, X-rays cannot penetrate certain materials, such as lead, iron, stainless steel, etc.
Post time: Apr-12-2024